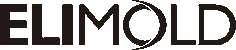I would like to start the article by quoting a famous saying to illustrate the importance of injection mold cooling systems: “Time is money.” If you are engaged in business, you will feel that time is of the essence, and you cannot waste precious time. In the same way in the process of injection molding, the most time-wasting part of the manufacturing cycle of injection molding is cooling.
In plastic injection molding, temperature directly affects the quality and efficiency of product manufacturing. High temperatures can prolong cooling time, affect productivity, and possibly affect the design performance of the final product. Too low a temperature can also affect the flow of the melt, thus affecting the design shape of the final product. Therefore, the temperature of the mold must be strictly controlled during the design of the injection mold. Reducing this temperature component will allow your manufacturing operation to produce more products in less time.
To achieve the shortest cooling time for injection molds, we first need to understand what an injection mold cooling system is, the common types of cooling designs, and its design specifications, principles, etc. To understand what is most important, please read more about this article. We will talk about several key issues above.
What is an injection mold cooling system?
Mold cooling systems include: cooling water temperature, mold temperature controller, and heating elements. The purpose of their work is not only to cool the mold but also to dissipate the high temperature brought to the mold by the molten plastic particles during the molding process so that the mold can maintain the temperature range designed for the performance of the product to be molded, in order to control the cooling rate of the plastic products in the cavity, thus improving the injection molding performance and production efficiency.
Definition of mold cooling system: A mold cooling system is a waterway system opened in the mold, which is connected to the external water source, and according to the design standards of different molded products, one or more water circuits are formed in the mold.
The main function of the mold cooling system: the designed waterway passes into the coolant and makes the coolant flow in a continuous cycle, thus bringing the excess heat in the mold outside the mold.
The main process of injection molding is to inject the high-temperature molten plastic into the low-temperature mold by high pressure and then cool and cure it to get the desired product. From a production point of view, the molding cycle is an important part of the process. However, 70% of the molding cycle is spent on product cooling.
Whether the mold temperature is controlled to a reasonable range is directly related to the dimensional accuracy, appearance, and internal quality of the product, as well as the production efficiency of the molded part and the achievement of the design requirements.
If the mold temperature is too high, the molding shrinkage is large, and the deformation rate of the molded part is large after demolding, it is also easy to cause overflow and sticky mold.
If the mold temperature is too low, the melt flowability is poor, the contour of the plastic part is not clear, and the surface will produce obvious defects such as silver wire or flow lines.
When the mold temperature is not uniform, the temperature difference between the inlet and the mold kernel will lead to uneven shrinkage of the plastic part and warpage and deformation of the plastic part, which will affect the shape and dimensional accuracy of the product. Therefore, the cooling system is an important task in the design of the whole injection mold.
What are the common cooling methods for plastic molds?
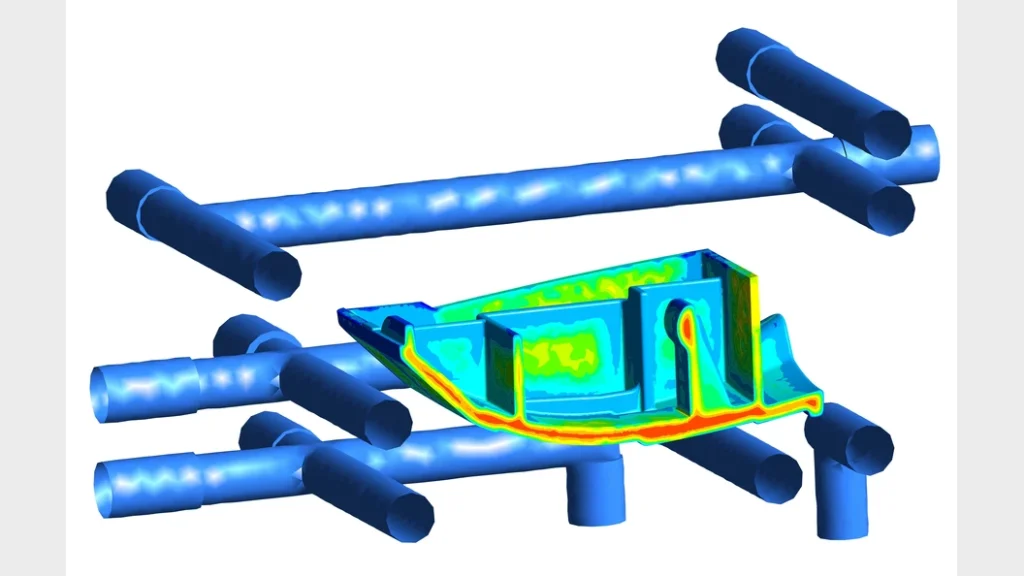
1、In the mold design, for the products with small height drops or flat shapes, the cooling is usually done by the return waterway, as shown in the following figure:
2、For the products with a small height difference but long length direction, the cooling method of adding water well in the middle of the zigzag waterway is used, as shown in the following figure:
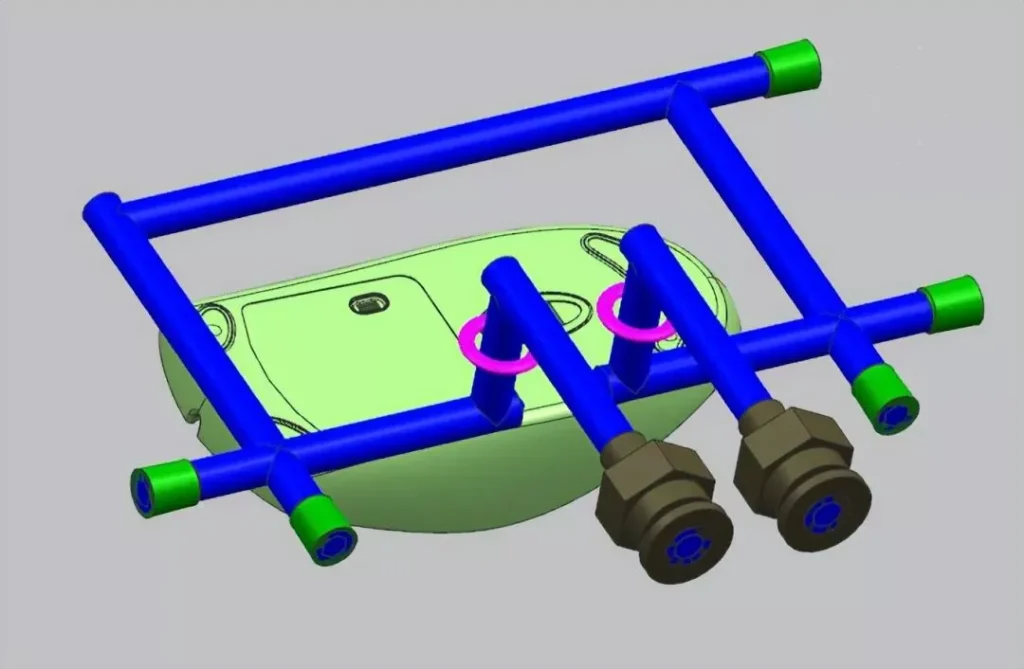
3、Some products have a large height difference, resulting in the zigzag waterway can not achieve the effect of cooling, then usually use the ordinary water transportation plus water well cooling method, as shown in the following figure:
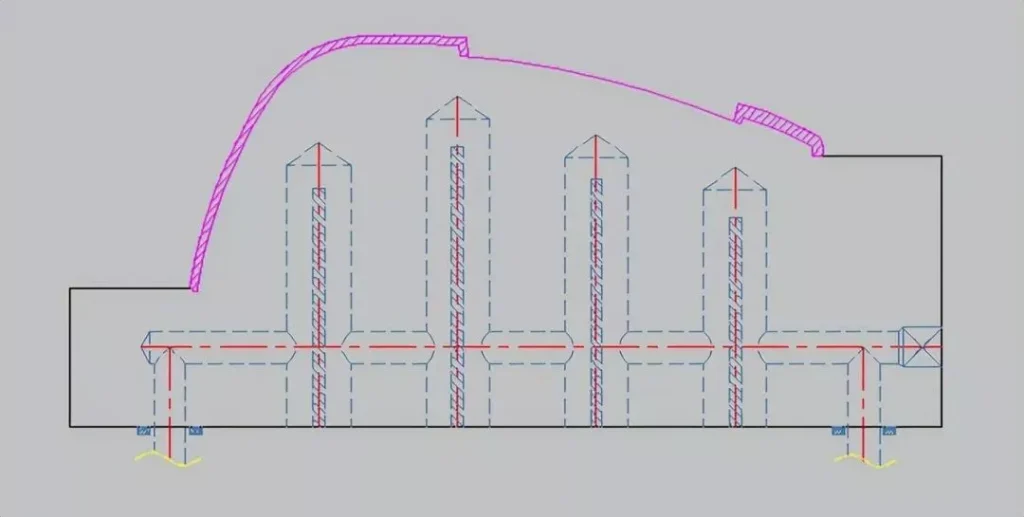
4、Some products with long and slender cores and high appearance requirements need to be cooled by water transportation of the nozzle type, as shown in the following figure:
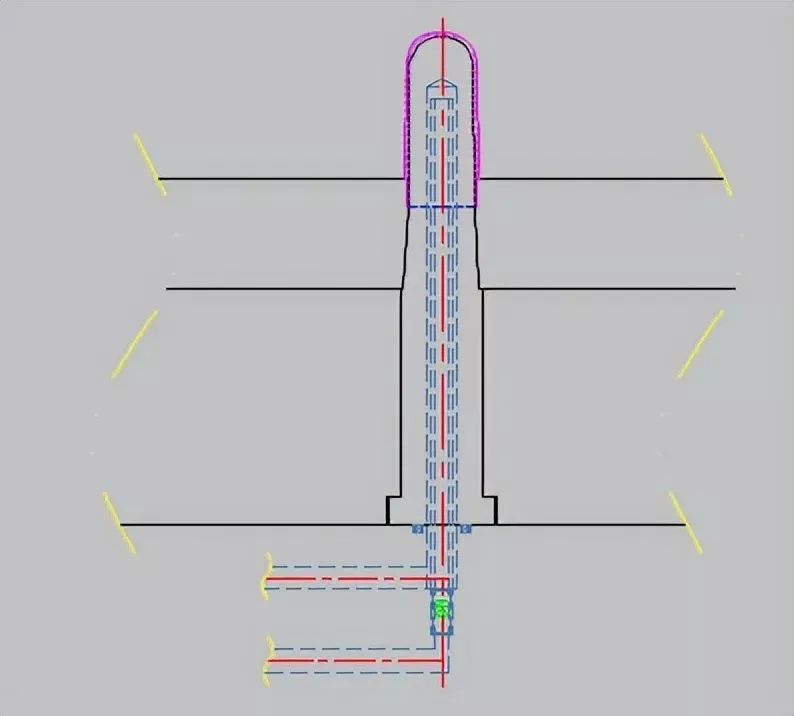
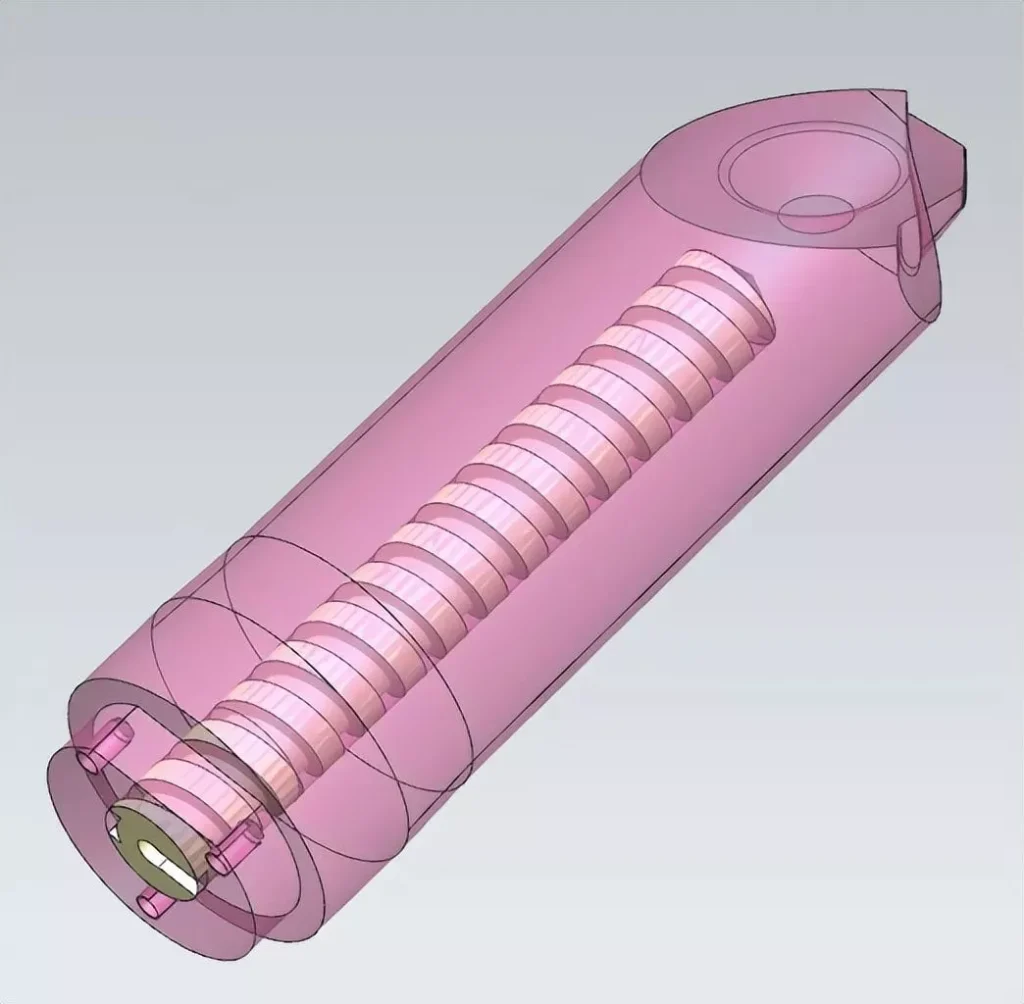
5、For some longer cores, to ensure the cooling effect, in addition to water well cooling, spiral water transportation cooling can also be used, as shown in the following figure:
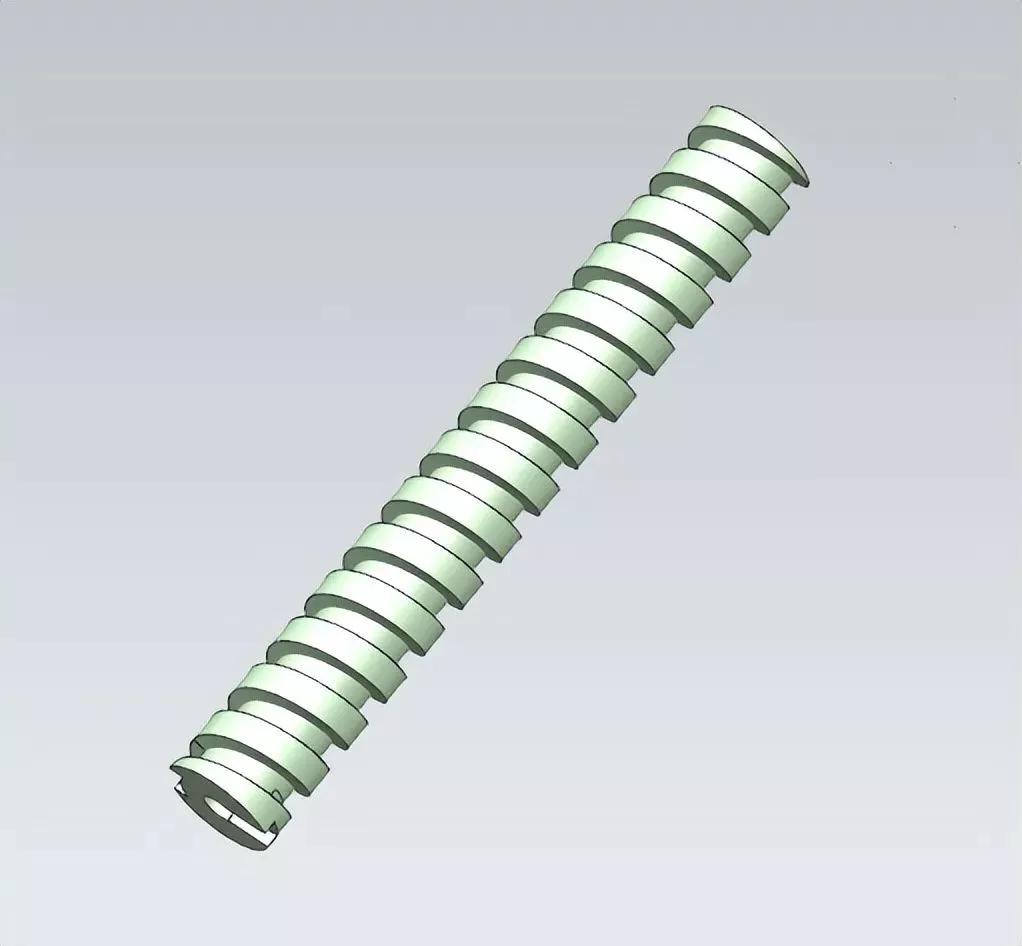

Design principles of cooling system for injection mold
To improve the efficiency of the cooling system and make the surface temperature of the cavity evenly distributed, the following principles should be followed in the design of the cooling system:
1. When designing the mold, the cooling method and the location of the cooling circuit should be considered first, and sufficient space should be left. The state of water flow in the cooling water circuit is turbulent flow. The setting of the cooling water circuit should meet the design needs of the product forming to ensure a sufficient, uniform, and balanced cooling effect.
2. Consider the temperature difference between the import and export, flow pressure drop (calculate the pipe diameter and length)
a.Reduce the temperature difference at the entrance and exit of cooling water (5℃ for general mold, 2℃ for precision mold).
b.The length of the cooling circuit is below 1.2-1.5m.
c.The flow rate is controlled within the range of 0-1.0m/s.
d. The number of circuit elbows does not exceed 15.
e.The number of turns is four in a group when using water separators in series.
f.For medium and large molds, the cooling water pipe can be divided into several independent circuits to increase the flow of coolant, reduce pressure loss and improve heat transfer efficiency.
g. Use more and finer cooling pipes than separate large-diameter pipes for a better cooling effect.
3. The number of cooling water holes should be designed as much as possible. The aperture should be designed as coarse as possible (the size should be chosen according to the shape characteristics of the plastic parts and the mold structure, and the inner diameter of the water pipes and pipe joints should be comparable to the cooling holes). The number, interval, and distance to the surface of the molding space significantly influence the control of the mold temperature.
4. The mold temperature near the gate is high, so the cooling circuit should be arranged from inside (near the gate) to outside (far from the gate). The main flow part of the mold is often in contact with the nozzle of the injection molding machine; the temperature near the gate is relatively high, cooling should be strengthened, and if necessary, a separate cooling water channel should be designed.
5. Because the temperature at the fusion mark is the lowest, the cooling pipe should be avoided being set at the fusion part of the product. Otherwise, the temperature will drop, the fusion mark will be more serious, and the strength of the fusion part of the injection molding part will be lower.
6. Inlet and outlet pipe joints should be on the anti-operation side.
7. The dynamic and fixed mold’s cooling circuits should be separated. Pay attention to the cooling balance of the concave mold and core; the designer should pay special attention to the cooling effect of the core and must ensure that the injection molded parts are fully cooled and shrinkage balanced.

Design specification of cooling system for injection mold
In the mold design, to shorten the molding cycle, improve production efficiency and ensure product quality, the cooling of the mold is very important; mold cooling commonly used media are cold water, warm water, oil temperature, etc.; not all molds should be designed to cool water, some molds also need to be heated, this is because the molding process of plastic materials applied to different products is different, resulting in the mold design temperature is also different, the following To share a few points about Elimold’s water transport design standards.
1. Cooling system design principles: large mold cold rubber position; small mold cold internal mold. The edge of the water transportation is more than 4(mm) from the inserts or inserts of the line position. The edge of the water transport is 8-10, 10-12, 12-16 (mm), or more from the edge of the glue position. The water transport edge from the ejector, inserts, and screws edge distance 3, 4, 5 (mm) from the steel material edge: M6, M8 water transport 11mm; M10, M12 water transport 14mm. Two parallel water transport center distances≥ 25mm. Before the mold, pay attention to the cold glue-bit runner material.
2. commonly used water pipe diameters of 6mm, 8mm, 10mm, and 12mm, of which 6mm water pipe diameter is not commonly used due to the mold through the cooling water, mold production mold easy to rust, the smaller the diameter of the water, not convenient to clean up.
3. commonly used forms of water transport around the water, water cylinder water, fountain water, spiral water, combined water, etc., around the water suitable for some products, not the height of the product, the design of this water transport, the distance between the inlet and outlet water for the water diameter (3-5) times, water transport distance from the spacing of the rubber bit for 1.5 times the diameter of the water transport, in the design of the water transport after the mold, pay attention to the lock after the mold of large screws
4. Commonly used forms of water transportation are ring water cylinder water transportation, combined water transportation, etc. Water cylinder water transportation is suitable for some products with large height differences; when designing this kind of water transportation, we should pay attention to: the safety distance of water transportation from the rubber position is at least 15mm; this kind of water transportation is generally used together with ordinary water transportation.
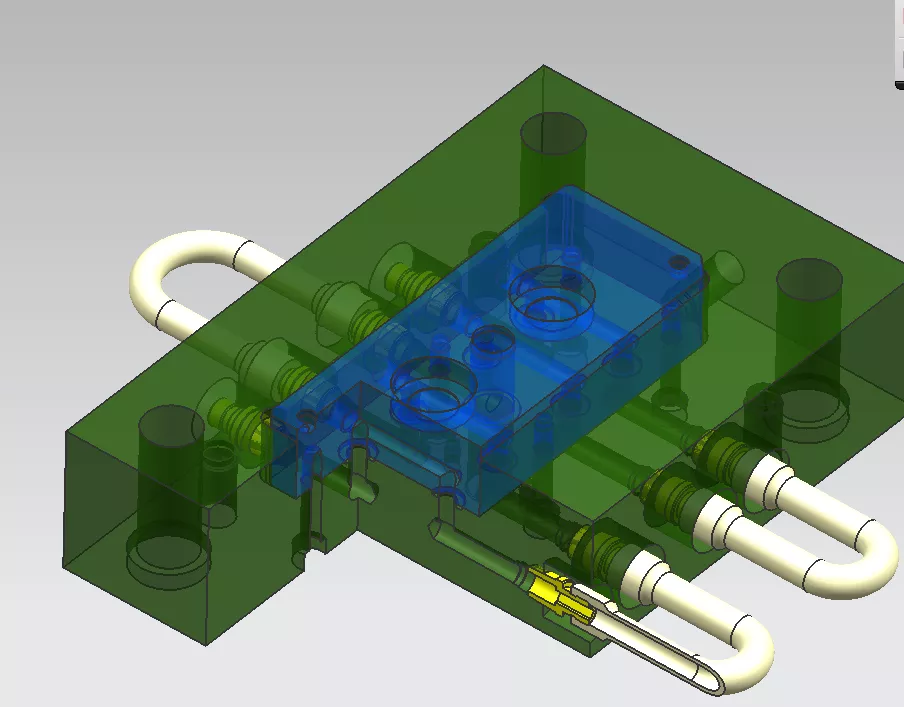
The importance of cooling in injection molding
Elimold knows the importance of cooling system design in injection molding. Our engineers work daily to optimize the cooling system design of our molds through study courses and peer-to-peer exchanges by our management system to optimize our technology for plastic parts production. Cooling takes up 70% of the entire plastic injection molding cycle, and proper design contributes to the success of plastic part projects.
For all your custom injection molded part manufacturing needs, Elimold has you covered. We enhance the productivity of custom plastic parts through smart, streamlined, automated manufacturing processes.
Simply put, Elimold is your partner of choice for custom manufacturing, delivering a faster, easier, and more efficient custom part production experience.
In other words, Elimold makes it possible to bring products like yours to market faster than ever.
Send your part drawings to [email protected], and our team will help you select the right materials and optimize your design. Our injection molding service can deliver samples in as little as 2 weeks!