Previously, Zenglong New Material Technology introduced the current development status and R&D trends of commonly used additive manufacturing (3D printing) materials in detail through two articles, “Common Materials and Forming Processes for Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)” and “R&D Trends of Common Materials for Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)”, and in this article, we will talk about the most cutting-edge materials with the most development potential worldwide.
3d printed hip bone. 3D-printed implants on white background.
Micro and nano additive manufacturing (3D printing) materials
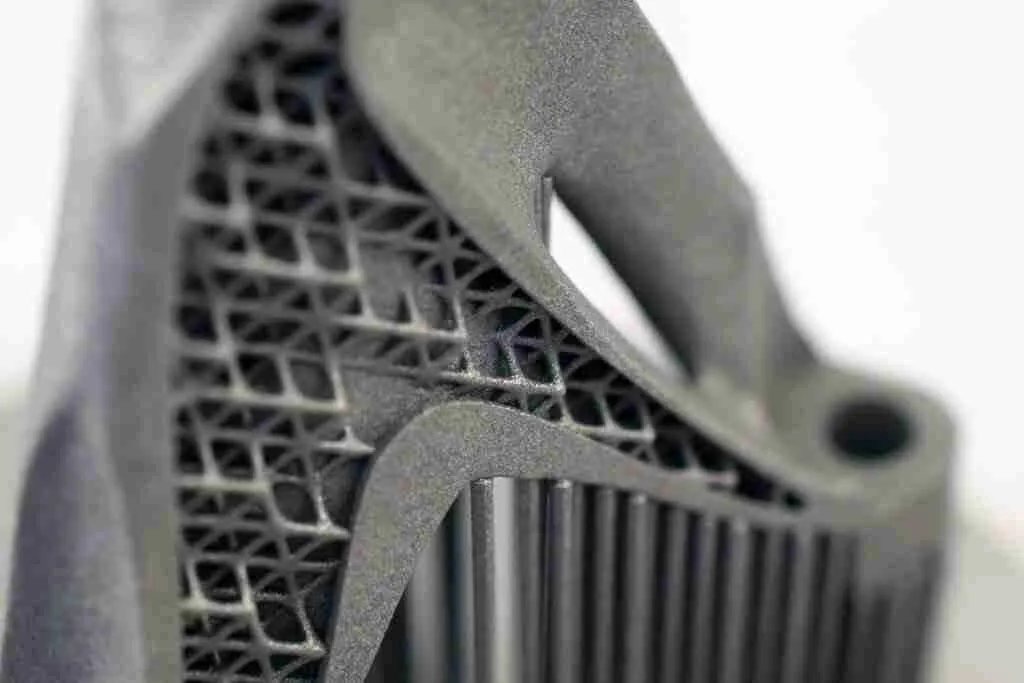
Micro and nano additive manufacturing is the technology of manufacturing millimeter, micron, and nanometer parts according to the principle of additive manufacturing (3D printing). The forming process of micro and nano additive manufacturing mainly includes micro and stereolithography, polymerization micro and nano 3D printing, aerosol jet 3D printing, direct ink writing (DIW), electrohydrodynamic jet printing, micro-selective laser sintering (μSLS), electrochemical manufacturing (EFAB), electric field drove jet deposition micro and nano 3D printing, etc.
The materials used for micro-nano additive manufacturing (3D printing) are mainly high-precision molecular materials, metal nanomaterials for micro-laser sintering, nano-conductive materials (nano-silver paste, graphene ink), nanoceramic powder, aerosol materials, degradable biomaterials, smart materials, etc.
1、High-precision molecular materials
A high-precision negative resin material developed by NanoScribe, Germany, has good electrical properties, mechanical properties, and thermal stability, with a certain degree of water resistance and low coefficient of thermal expansion, which can realize the printing of objects as small as 160nm in size. The surface cells designed by Professor Li Xiaoyan of Tsinghua University using the concept of force material science can prepare polymeric micron dot matrix materials based on very small surfaces by stereolithography and obtain pyrolytic carbon nanodot matrix materials by high-temperature pyrolysis, the usual size of which varies from a few hundred microns to several hundred nanometers.
2、Metallic nanomaterials
Metal nanomaterials include nanoparticle ink, ionic solutions, and molten metal droplets; these materials can be manufactured with a resolution <10μm metal structure; the current German 3D MicroPrint company can produce two sizes less than 5μm stainless steel powder material that can be used in the laser forming process, the U.S. Microfabricated company can produce four kinds of layered thickness in 5μm, the surface roughness at 0.8μm, which can be used for batch production of micro-scale metal parts.
The minimum feature size of a metal additive manufacturing (3D printing) part is influenced by the size of the material, which can be supplied in powder, wire, sheet, or inkjet form. Applicable to the powder forming processes, such as micro-selective laser melting (SLM) and laser engineering net forming process, can print 0.3-10μm metal powder particles; the final formed parts can be limited to the minimum feature size of about 20μm size.
3、Conductive materials
Conductive micro-nano materials are nano-silver ink and graphene materials; currently, the U.S. Nano Dimension company developed nano-silver conductive ink material that can reach 10 to 100nm, with silver content between 20% and 70%. Poland XTPL company developed “ultra-precision deposition” XTPL, a Polish company, has developed an “ultra-precision deposition” micro-additive manufacturing process that enables the printing of molded parts as small as 1 to 50 μm, which is used in the repair of circuit defects in smart glass displays.
Graphene is recognized as the world’s thinnest, strongest, and most flexible material, with superb thermal and electrical conductivity and cheaper than silver ink; the U.K.’s Haydale Graphene Company is currently researching graphene aerogel lightweight materials and graphene-reinforced PLA fiber materials for 3D printing.
4、Bio-micro-nano materials
Bio-micro-nano additive manufacturing (3D printing) materials are mainly synthetic biocompatible and degradable polymer materials and natural biomaterials, such as polylactic acid, polycaprolactone, levopolylactic acid, hydrogels, nanoceramics (medical grade), which can achieve micro-scale printing accuracy. A recent publication in the journal Bioactive Materials titled “Magnesium surface-activated 3D printed porous PEEK scaffolds for in vivoosseointegration by promoting angiogenesis and osteogenesis” describes the use of magnesium ion-chelated polydopamine (PDA) coatings, a biomicroscopic material that improves the hydrophilicity of PEEK-printed skeletal scaffolds, promotes cell proliferation and adhesion, and aids in bone cell differentiation. A concrete ink described in the journal Nature Communications, “In situ 3D bioprinting with concrete bio-ink”, in which cells are attached to a microgel substrate by electrojet, can repair tissue defects by in situ 3D printing.
5、4D printing of micro and nano smart materials
Micro-scale 4D printing is also one of the current research hotspots in additive manufacturing. The so-called “4D printing” is the automatic deformation of materials into the designed shape. Therefore, the materials in this field are mainly various smart materials, including deformation materials, shape-memory polymers, shape-memory alloys, stimulus-response materials, hydrogels, piezoelectric materials, etc.
These are the various materials in the micro and nano additive manufacturing field, in addition to some new materials suitable for conventional-size additive manufacturing (3D printing).
environmentally friendly materials
In the field of polymer materials, some researchers are working on developing bio-based materials or adding modifications to other materials to make recyclable or reusable materials; for example, UBQ Materials and Plastics App have collaborated to make filamentary materials for additive manufacturing (3D printing) from technical waste produced by the company. 100% biodegradable NonOilen material.
Cemented Carbide
Cemented Carbide is a consistent and extremely hard material formed by bonding carbon and carbide particles to composite materials with a metallic adhesive through adhesive spray 3D printing technology. Cemented Carbide can withstand the tremendous forces of grinding or drilling and produce wearable parts and tools through 3D printing technology, as well as produce shaped parts or internal cooling tunnels.
Fourth, concrete materials
Concrete materials 3D printing is achieved through the extrusion process; the extruded material directly accumulates on the lower material in the absence of a mold for support to maintain the shape, the need to consider the rheology of the material; research has shown that the addition of materials such as cellulose ether, concave clay, fly ash, silica fume, and water reducing agents can effectively improve the rheology of concrete materials, and currently, according to the different materials added to these, the formation of silicate cement system, sulfoaluminate cement system, phosphate cement system, geopolymer system, and magnesium alumina cement system.