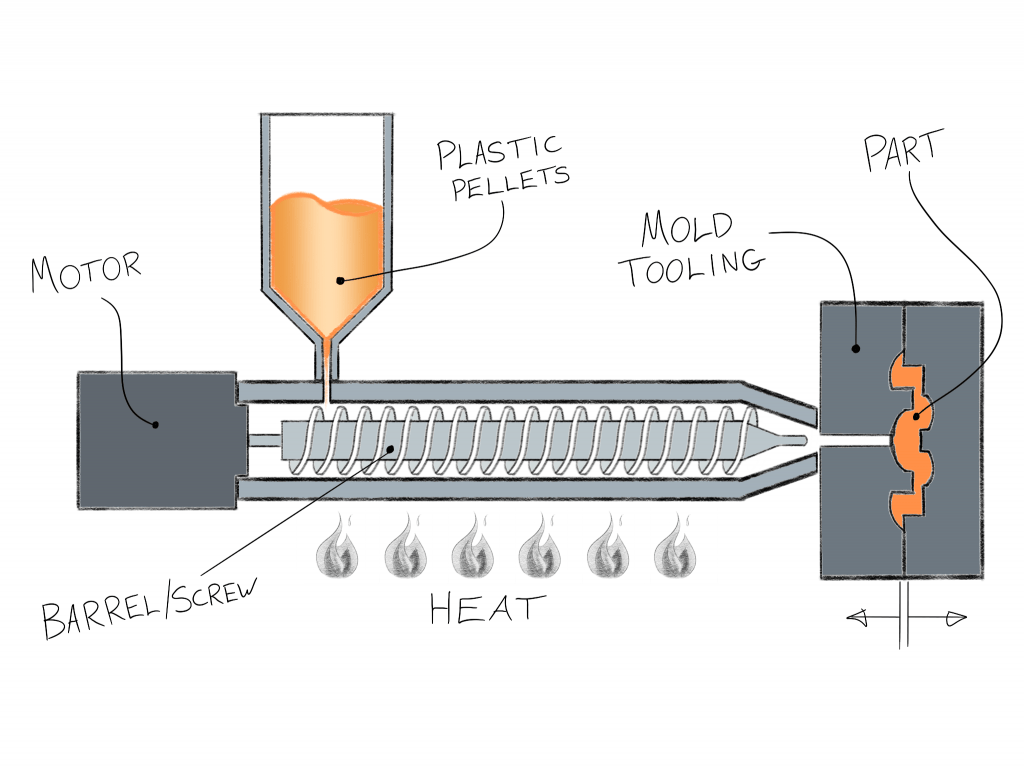
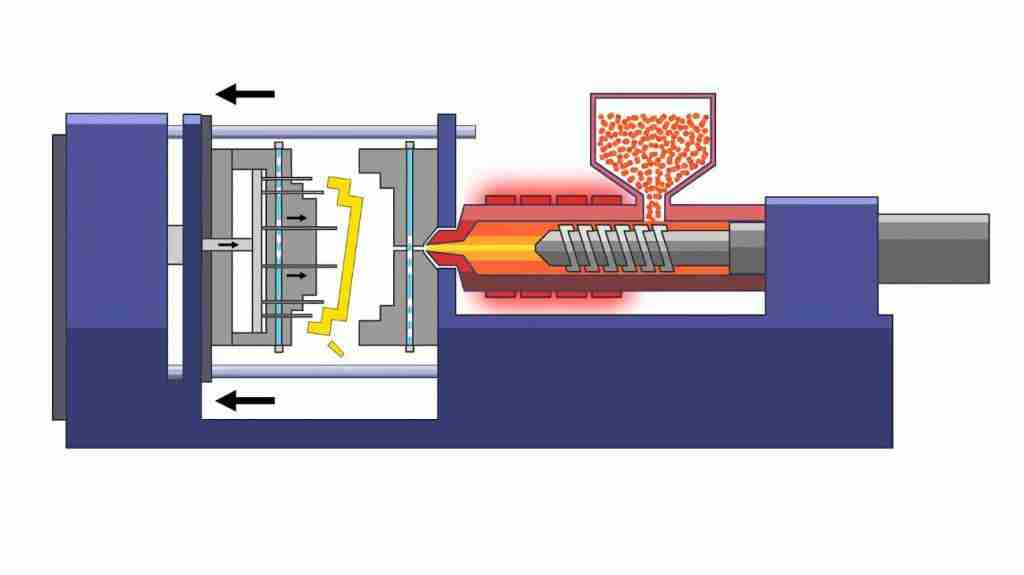
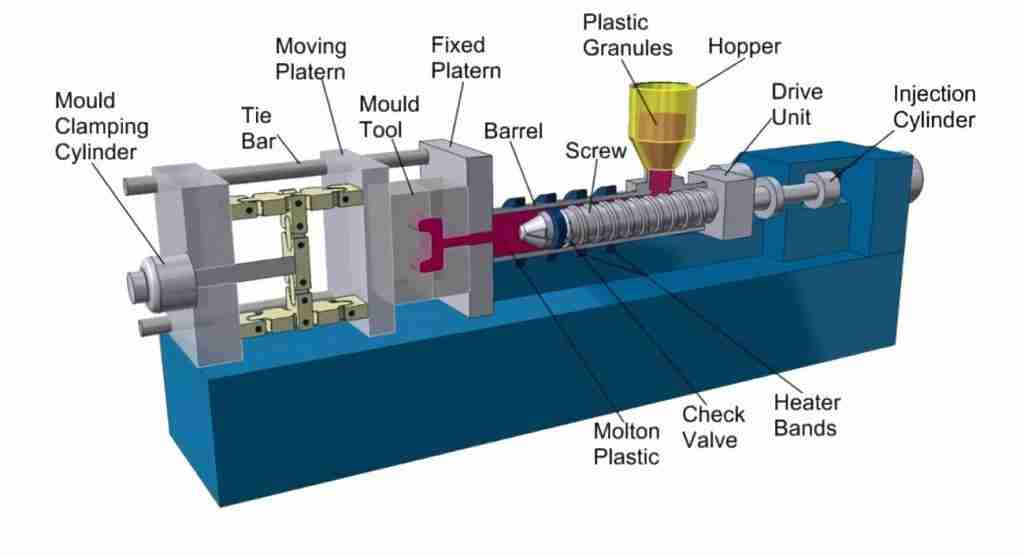
(1) Injection molding
Injection molding: Also known as injection molding, its principle is to add granular or powdery raw materials into the hopper of the injection machine, and the raw materials are heated and melted into a flowing state. The system enters the mold cavity and hardens and forms in the mold cavity. Factors affecting the quality of injection molding: injection pressure, injection time, and temperature.
Process features:
Advantage:
1. Short molding cycle, high production efficiency, and easy automation
2. It can form plastic parts with complex shapes and precise dimensions, with metal or non-metal inserts
3. Stable product quality
4. Wide range of adaptation
shortcomings:
1. The price of injection molding equipment is higher
2. The structure of the injection mold is complex
3. The production cost is high, the production cycle is long, and it is not suitable for the production of single and small batches of plastic parts
application:
Among industrial products, injection-molded products include kitchen supplies (garbage cans, bowls, buckets, pots, cutlery, and various containers), housings for electrical equipment (hair dryers, vacuum cleaners, food mixers, etc.), toys and games, automobiles, Various industrial products, parts of many other products, etc.
(2) Insert injection molding
Insert injection molding: Insert molding refers to the molding method of inserting pre-prepared inserts of different materials into the mold and then injecting resin. The molten material is bonded and solidified with the inserts to form an integrated product.
Process features:
1. The pre-molding combination of multiple inserts makes the post-engineering of the product unit combination more rational.
2. The combination of the easy formability and flexibility of resin and the rigidity, strength, and heat resistance of metal can make complex and exquisite metal-plastic integrated products.
3. In particular, by combining resin’s insulating properties and metal’s electrical conductivity, the formed products can meet the basic functions of electrical products.
4. For rigid molded products and bending elastic molded products on the rubber gasket plate, after the integrated products are made by injection molding on the substrate, the complicated operation of arranging the sealing rings can be omitted, which makes the automatic combination of the subsequent processes easier.
(3) Two-color injection molding
Two-color injection molding: refers to the molding method of injecting two different color plastics into the same mold. It can make the plastic appear in two different colors and make the plastic parts present regular patterns or irregular moiré-like colors to improve the usability and aesthetics of the plastic parts.
Process features:
1. The core material can use low viscosity to reduce the injection pressure.
2. The core material can use recycled secondary materials for environmental protection.
3. According to different use characteristics, for example, soft material is used for the skin material of thick finished products, hard material is used for the core material, or foamed plastic can be used for the core material to reduce the weight.
4. Lower-quality core materials can be used to reduce costs.
5. The skin or core material can be expensive and have special surface properties, such as anti-electromagnetic wave interference, high electrical conductivity, and other materials to increase product performance.
6. Appropriate combination of skin and core material can reduce residual stress of molded products and increase mechanical strength or product surface properties.
(4) Micro-foaming injection molding process
Micro-foaming injection molding process: It is an innovative precision injection molding technology that relies on the expansion of pores to fill the product and completes the molding of the product under low and average pressure. The microcellular foam molding process can be divided into three stages: first, the supercritical fluid (carbon dioxide or nitrogen) is dissolved into the hot melt adhesive to form a single-phase solution; then, the mold type with lower temperature and pressure is injected through the switch-type nozzle. Due to the molecular instability caused by the decrease in temperature and pressure, many bubble nuclei are formed in the product. These bubble nuclei gradually grow to form tiny pores.
Process features:
1. Precision injection molding;
2. Breaking through many limitations of traditional injection molding, it can significantly reduce the weight of parts and shorten the molding cycle;
3. Greatly improve the warpage deformation and dimensional stability of the parts.
Application:
Car dashboards, door panels, air-conditioning ducts, etc.
(5) Nano Injection Molding (NMT)
NMT (NanoMoldingTechnology): It is a method of combining metal and plastic with nanotechnology. After the metal surface is treated by nanotechnology, the plastic is directly injection molded on the metal surface so that the metal and plastic can be integrally formed. Nanomolding technology is divided into two types of processes according to the location of the plastic:
1. Plastic is the integral molding of non-appearance surface
2. Plastic is the integral molding of the appearance surface
Process features:
1. The product has a metallic appearance and texture,
2. The design of the parts of the product machine is simplified, making the product lighter, thinner, shorter, smaller, and more cost-effective than the CNC machining method.
3. Reduce production cost and high bonding strength and greatly reduce the utilization rate of related consumables
Applicable metal and resin materials:
1. Aluminum, magnesium, copper, stainless steel, titanium, iron, galvanized sheet, brass;
2. The adaptability of aluminum alloy is strong, including the 1000 to 7000 series;
3. Resins include PPS, PBT, PA6, PA66, and PPA;
4. PPS has a particularly strong adhesive strength (3000N/c㎡).
Application:
Mobile phone case, laptop case, etc.
(6) Blow molding
Blow molding: The molten thermoplastic raw material extruded from the extruder is clamped into the mold, and the air is blown into the raw material. The molten raw material expands under air pressure, fits into the mold cavity wall, and finally cools. The method of curing into the desired product shape. Blow molding is divided into film blow molding and hollow blow molding:
1. Film blow molding
Film blow molding is to extrude molten plastic from the annular gap of the extruder die into a thin cylindrical tube and, at the same time, blow compressed air into the inner cavity of the thin tube from the center hole of the die to inflate the thin tube to a diameter A larger tubular film (commonly known as a bubble tube), which is coiled after cooling.
2. Hollow blow molding
Hollow blow molding is a secondary molding technology that inflates a rubber-like parison closed in a mold cavity into a hollow product using gas pressure and is a method for producing hollow plastic products. According to the different manufacturing methods of the parison, hollow blow molding includes extrusion blow molding, injection blow molding, and stretch blow molding.
1) Extrusion blow molding: Extrusion blow molding is to extrude a tubular parison with an extruder, clamp it in the mold cavity and seal the bottom. At the same time, it is hot and then blows compressed air into the inner cavity of the tube blank for inflation.
2) Injection blow molding: The parison is obtained by injection molding. The parison is left on the core mold of the mold. After the blow mold is used to close the mold, compressed air is introduced into the core mold to inflate and cool the parison. After demolding, the product is obtained.
Advantage:
The product’s wall thickness is uniform, the weight tolerance is small, the post-processing is less, and the waste corner is small; it is suitable for producing small refined products with large batches.
3) Stretch blow molding: The parison that has been heated to the stretching temperature is placed in the blow mold, longitudinally stretched with a stretch rod, and transversely stretched with blown compressed air to obtain the product’s method.
Application:
1. Film blow molding is mainly used to manufacture thin plastic molds;
2. Hollow blow molding is mainly used to make hollow plastic products (bottles, packaging barrels, watering cans, fuel tanks, cans, toys, etc.).
(7) Extrusion molding (profiles)
Extrusion molding: Also known as extrusion molding, it is mainly suitable for the molding of thermoplastics and also suitable for molding some thermosetting and reinforced plastics with good fluidity. The molding process uses the rotating screw to extrude the heated and melted thermoplastic raw material from the head with the desired cross-sectional shape, then shape it by the shaper, and then pass it through the cooler to make it harden and solidify to become the desired cross-sectional shape. Product.
Process features:
1. Low equipment cost;
2. The operation is simple, the process is easy to control, and it is convenient to realize continuous automatic production;
3. High production efficiency; uniform and dense product quality;
4. Products or semi-finished products with various cross-sectional shapes can be formed by changing the die’s die.
Application:
In the field of product design, extrusion molding has strong applicability. The extruded products include pipes, films, rods, monofilaments, flat belts, nets, hollow containers, windows, door frames, sheets, cable cladding, monofilaments, and other profiles.
